Ohm’s Law: The Fundamental Relationship in Electrical Circuits
Ohm’s Law stands as a cornerstone in the realm of electrical engineering, providing a fundamental relationship that governs the behavior of electrical circuits.
This law, named after the German physicist Georg Simon Ohm, succinctly describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance. In this exploration,
we will delve into the intricacies of Ohm’s Law, its mathematical representation, practical applications, and its significance in understanding and designing electrical systems.
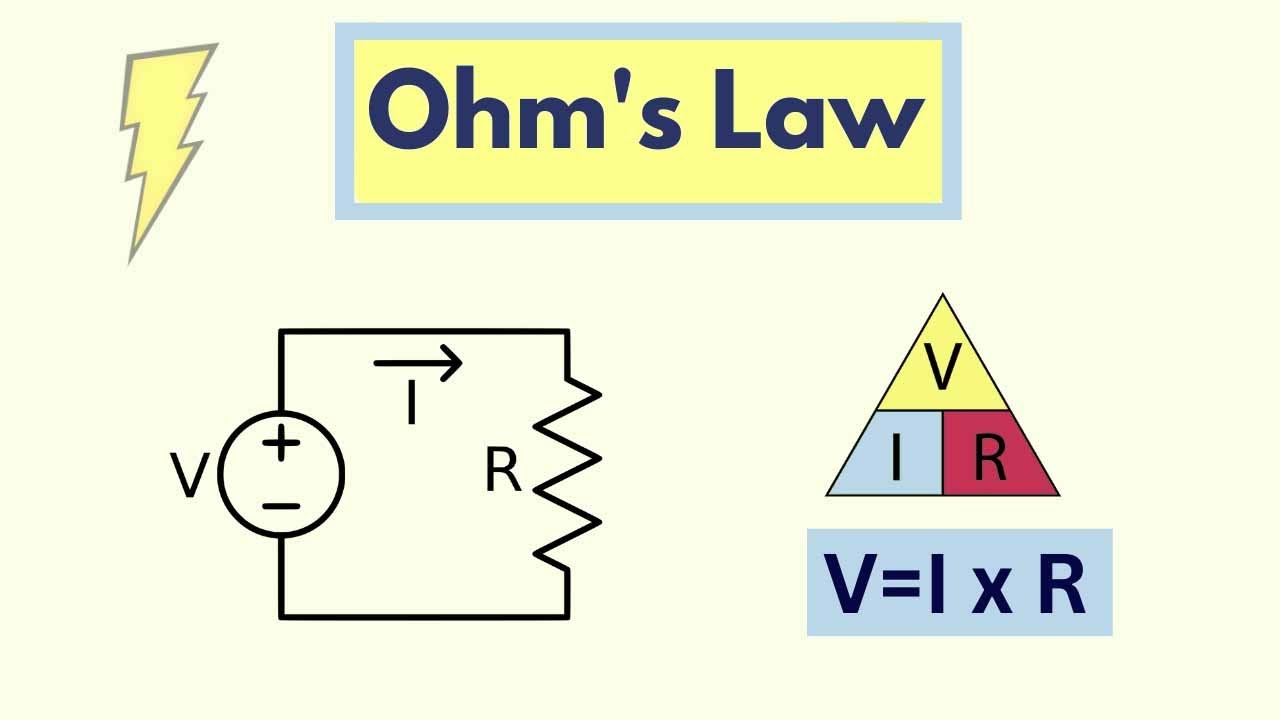
Ohm’s Law Equation:
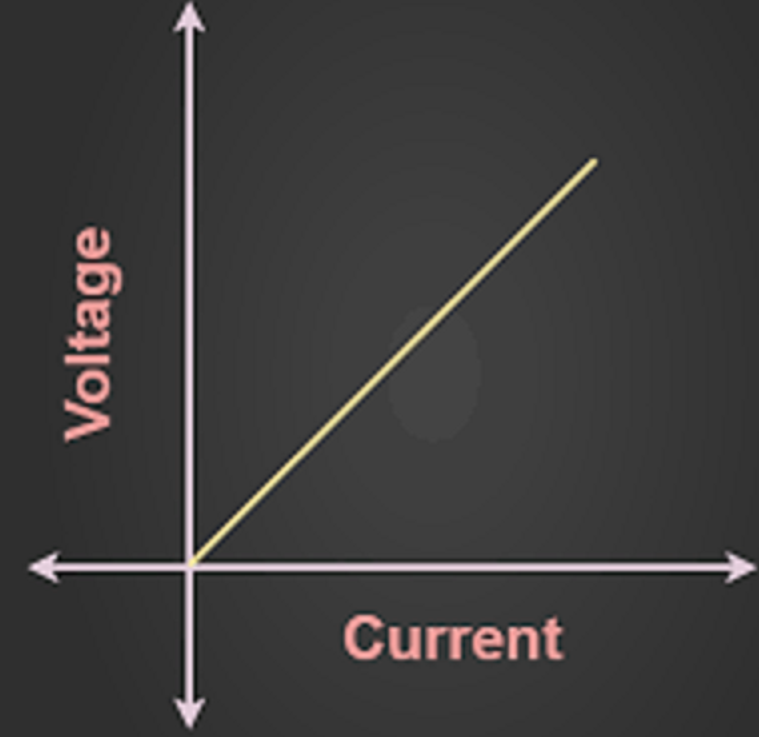
At its core, Ohm’s Law is represented by a simple mathematical equation: V = I * R. Here, V represents voltage, I stands for current, and R denotes resistance. The equation reveals that the voltage across a conductor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it, with resistance acting as the proportionality constant.