Maxwell’s relations are a set of four important thermodynamic equations derived from the fundamental laws of thermodynamics.
Named after the Scottish physicist James Clerk Maxwell, these relations provide valuable insights into the relationships between different thermodynamic properties of a system.
Maxwell’s relations are particularly useful for simplifying calculations and understanding the interdependence of thermodynamic variables.
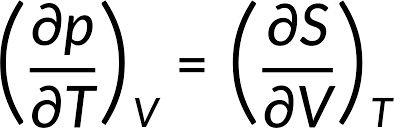
The First Relation:
(∂P/∂T)S=−(∂S/∂V)P
This relation involves the partial derivatives of temperature , pressure , volume , and entropy . It relates how the temperature changes with respect to pressure at constant entropy to the rate at which volume changes with respect to entropy at constant pressure.
The Second Relation:
(∂V/∂T)S=(∂S/∂P)V
This relation connects the partial derivatives of temperature, volume, pressure, and entropy. It illustrates how the rate at which temperature changes with respect to volume at constant entropy is related to the rate at which pressure changes with respect to entropy at constant volume.
An important application of the second Maxwell’s relation is in the calculation of the isothermal compressibility (), which measures the response of a substance to changes in pressure at constant temperature
The Third Maxwell’s Relation:-
(∂V/∂S)T=(∂T/∂P)V
This relation involves the partial derivatives of entropy, volume, pressure, and temperature. It relates how the rate at which entropy changes with respect to volume at constant temperature is related to the rate at which pressure changes with respect to temperature at constant volume.
The Fourth Maxwell’s Relation:-
(∂T/∂P)V=−(∂V/∂S)T
For More information visit web :-https://xeidea.com/
And news website:– https://lokprasang.com/

