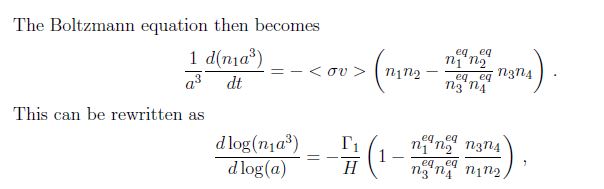The Boltzmann equation is a fundamental concept in statistical mechanics, describing the behavior of a gas at the molecular level. Named after the Austrian physicist Ludwig Boltzmann, the equation provides a statistical foundation for understanding the relationship between macroscopic observables, such as temperature and pressure, and the microscopic motions of individual particles in a gas.
Boltzmann Equation:-
the Boltzmann equation connects the statistical properties of a gas to its thermodynamic behavior. It is a partial differential equation that describes the time evolution of the single-particle distribution function, which gives the probability density of finding a particle with a specific position and momentum in phase space.
The Boltzmann equation is particularly important for understanding the behavior of dilute gases, where the interactions between individual particles dominate. In such systems, particles move freely and collide with each other, exchanging energy and momentum. The Boltzmann equation accounts for these collisions and provides a way to predict how the gas properties, such as temperature and pressure, evolve over time.
The equation itself is written as follows:-
The left-hand side of the equation describes the advection and external force effects on the distribution function, representing the motion of particles in response to external forces. The right-hand side, the collision term, encapsulates the effects of particle collisions on the distribution function. The Boltzmann equation is a balance between these two opposing forces: the deterministic evolution due to advection and external forces and the stochastic changes arising from collisions.
Solving the Boltzmann Equation:-
Equation is a challenging task due to the complexity of the collision term, which involves multiple particle interactions. Simplified models, such as the BGK (Bhatnagar-Gross-K rook) model, have been proposed to make the equation more tractable. These models retain the essential features of the collision term while making analytical and numerical solutions more feasible.
The Boltzmann equation’s implications are vast and extend to various fields, including fluid dynamics, plasma physics, and astrophysics. In fluid dynamics, for example, the Boltzmann equation serves as the foundation for the kinetic theory of gases, linking microscopic particle behavior to macroscopic fluid properties.
Moreover, the Boltzmann equation provides a bridge between the microscopic world of particles and the macroscopic world of thermodynamics. It connects the statistical mechanics of individual particles to the observed thermodynamic properties of gases, such as temperature and pressure. This connection is crucial for understanding how the macroscopic behavior of a gas emerges from the collective motion of its constituent particles.
In summary, the equation is a cornerstone of statistical mechanics, providing a framework for understanding the behavior of gases at the molecular level. Its mathematical expression captures the interplay between deterministic advection and external forces and the stochastic effects of particle collisions. While solving the Boltzmann equation is a complex task, its applications extend across various scientific disciplines, making it a key concept in the study of the physical world.
टकराव शब्द की जटिलता के कारण समीकरण एक चुनौतीपूर्ण कार्य है, जिसमें कई कणों की परस्पर क्रिया शामिल होती है। समीकरण को और अधिक सुगम बनाने के लिए बीजीके (भटनागर-ग्रॉस-के रूक) मॉडल जैसे सरलीकृत मॉडल प्रस्तावित किए गए हैं। ये मॉडल विश्लेषणात्मक और संख्यात्मक समाधानों को अधिक व्यवहार्य बनाते हुए टकराव शब्द की आवश्यक विशेषताओं को बरकरार रखते हैं।
बोल्ट्ज़मैन समीकरण के निहितार्थ विशाल हैं और द्रव गतिकी, प्लाज्मा भौतिकी और खगोल भौतिकी सहित विभिन्न क्षेत्रों तक विस्तारित हैं। उदाहरण के लिए, द्रव गतिकी में, बोल्ट्ज़मान समीकरण गैसों के गतिज सिद्धांत की नींव के रूप में कार्य करता है, जो सूक्ष्म कण व्यवहार को स्थूल द्रव गुणों से जोड़ता है।
इसके अलावा, बोल्ट्ज़मैन समीकरण कणों की सूक्ष्म दुनिया और थर्मोडायनामिक्स की स्थूल दुनिया के बीच एक पुल प्रदान करता है। यह व्यक्तिगत कणों के सांख्यिकीय यांत्रिकी को तापमान और दबाव जैसे गैसों के देखे गए थर्मोडायनामिक गुणों से जोड़ता है। यह संबंध यह समझने के लिए महत्वपूर्ण है कि गैस का स्थूल व्यवहार उसके घटक कणों की सामूहिक गति से कैसे उभरता है।
संक्षेप में, समीकरण सांख्यिकीय यांत्रिकी की आधारशिला है, जो आणविक स्तर पर गैसों के व्यवहार को समझने के लिए एक रूपरेखा प्रदान करता है। इसकी गणितीय अभिव्यक्ति नियतात्मक संवहन और बाहरी ताकतों और कण टकराव के स्टोकेस्टिक प्रभावों के बीच परस्पर क्रिया को पकड़ती है। हालाँकि बोल्ट्ज़मैन समीकरण को हल करना एक जटिल कार्य है, इसके अनुप्रयोग विभिन्न वैज्ञानिक विषयों तक फैले हुए हैं, जो इसे भौतिक दुनिया के अध्ययन में एक महत्वपूर्ण अवधारणा बनाता है।
For More information visit web :-https://xeidea.com/
And news website:– https://lokprasang.com/